Glossary of Terms
Jump to a corresponding letter: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A
ABS
American Bureau of Shipping; an independent vessel classification society that establishes criteria standards/rules, for design, construction and periodical survey of marine vessels and offshore structures to promote the security of life, property and the natural environment.
Admeasure
To measure, calculate and certify certain dimensions of a vessel as well as its gross and net tons for the purpose of registration.
Affreightment Order
Document utilized to evidence agreement of the specific affreightment-based economic considerations and special provisions for a single voyage booked under a Master Contract.
Aground
When a boat or barge is stranded in shallow water.
AHP
Above Head of Passes; used with mileage designations on the Mississippi River, the Head of Passes being mile zero.
Airline Respirator
For the purposes of the hydrogen sulfide SOP, this type of respirator is one supplied with breathing air from a remote bottled air source. The respirator mask is a full face pressure-demand model with a five minute escape air supply attached. The airline hose supplying the mask is to be a breathing air hose. The length of the hose from the bottled air source to the mask cannot exceed 300 ft. in length.
AIWW
Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway. A series of federally maintained navigation channels from Norfolk, Virginia to Miami, Florida.
Allowed Downtime
Time allowed by contract to do necessary repairs to equipment without being taken off the payroll.
Amendment
An addition, change, correction, or revision, to a contract; a list or section consisting of added or changed material.
Anchor Billboard
A structure on the deck of a vessel upon which the anchor is mounted when not in use.
Anodes
Metallic plates which, when attached to the hull of a vessel, decompose because of electrolysis, thereby reducing deterioration of hull plate. Zinc anodes are used on steel vessels and Magnesium anodes are used on Aluminum vessels. The radius of coverage/protection depends on the size of the anode.
Athwart ship
Transverse or across a vessel from side to side.
AWO
American Waterways Operators – a trade organization made up of marine companies using the waterways of the United States and companies related to that industry.
B
Back Haul
When a tow is booked to move product from point A to point B and then reloaded at point B or a dock close by. Usually the two trips are for different customers.
Ballast
Any substance, other than cargo, that is usually placed in the inner compartment of a vessel to produce a desired draft or trim. Liquid ballast can affect the overall stability of any vessel.
Bareboat Charter
(Demise Charter) A form of vessel rental in which the charterer assumes total responsibility for the vessel and its operations as if it were his own.
Barge Charter
A contract for the commercial leasing of a barge or space on a barge.
Barge Loading Plan
Instructions for loading communicated (verbally and/or written) to the attending vessel or Shore Tankerman prior to a bunker barge loading.
Barrel
42 U.S. gallons at 60 degrees Fahrenheit.
Beam
The breadth of a vessel.
Bell Suction
The flared open end of a cargo pipeline, inside the barge, which is situated close to the bottom of a liquid cargo tank. This facilitates/allows the pump to maintain suction and strip almost the entire product from a barge.
Benzene Mixture
Cargoes containing a minimum of one half of one percent (0.5%) of benzene by volume. All workers working around benzene must have proper training with respirator equipment.
Berth
A space for docking.
Bilge
The lowest inner space of a vessel’s hull.
Bin
A walled enclosure built on the deck of a barge for the purpose of retaining cargo; also called a pen or cargo box.
Bitt (Bollard or Timberhead)
A single or double post on a vessel or wharf to which lines or cables are secured. These are commonly found on all 4 corners of a barge.
Boat Charter
Terms by which a boat is chartered in or chartered out. Terms of the contract could include rate, crew, fuel cost, and a description of the job.
Boilerplate
Term used to describe standard language in a legal document that is identical in instruments of a like nature.
Bollard Pull
The static pulling force of a tugboat measured in pounds. This is usually measured by attaching a tow line to a dockside bollard and measuring the force (tons) of pull against the dock. There are special parameters associated with this test such as the length of the line, the water depth, sea state, etc. This is typically listed in specification of offshore tugs.
Bottoms
Product that is left onboard a barge after discharging. Bottoms, also refers to the previous cargo carried in the barge.
Bounding Angle
A steel angle used for reinforcement at the junction of two steel plates.
Bow
The forward or front end of a vessel.
Box
The end of a barge, which is squared for the full depth and width of the hull otherwise called a square stern.
Breadth
Distance from side to side; full width.
Break Tow
To disassemble a tow
Bridle
A V-shaped chain, wire, or rope attached to a vessel being towed to which the towline is connected.
Brokerage
When outside equipment is chartered in to move product for a customer. This could be an affreightment or a fully-found affreightment.
Buck Frame
A transverse truss frame inside a barge commonly consisting of one upper and lower horizontal steel beam connected to each other with various diagonal and vertical steel members.
Bunker
Fuel used by a ship; or tows that deliver fuel supply to ships.
Bulkhead
An upright partition or wall separating compartments in a barge. Usually the strongest vertical load bearing point on a barge.
Bulwark
The side of a vessel that extends above the main deck.
Bunker Boats
Boats which are dedicated to handling jobs for the bunker operation.
Bunker Receipt
A document which shows the types and quantities of fuel a ship received, to be signed by the Chief Engineer to guarantee payment to the fuel supplier.
Buoy
A stationary floating object used as an aid for navigation. Different shapes, colors and lighting have different meanings for navigation.
Butterworth
A tank cleaning process or device designed and patented by Arthur Butterworth in the early 1920’s. Resembling a heavy duty industrial sprinkler it is dropped down inside a barge, through a small opening or hatch, and sprays the entire internal surface of the tank, with hot or cold water and or chemicals, for cleaning.
Butterworth Opening
A deck access opening with bolted cover, designed for butterworth operations.
C
Calcium
Chlorinated lime, toxic by inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption.
Calcium Hypochlorite
Chlorinated lime, toxic by inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption. Avoid exposure and use caution when handling this material.
Camber
The upward slope of a vessel’s deck, occurring when the centerline is higher than the gunwale. Also referred to as a “dead-rise in the deck”.
Camel
A pontoon used to fender between a vessel and a wharf.
Capstan
A hand or machine powered, vertical or horizontal spindle-mounted drum which rotates and pulls lines by winding.
Cargo Flush
Cargo that is loaded over previous cargo to rid tanks of cargo bottoms. Once the flush is completed it is then pumped back to the dock facility.
Cat Feed
A dirty product generally used as a fuel for cat cracker units in a refinery. Some barge cleaning facilities will use cat feed as fuel in their boilers used to heat water for cleaning.
CERCLA
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act. The U.S. federal statute that establishes the legal and financial responsibilities of those persons or companies which discharge or dispose of hazardous substances on or into land, air, and navigable waters of the U.S. Primarily administered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Certificate of Inspection (COI)
A document issued by the U.S. Coast Guard after they have inspected any vessel that is certified by the United States Coast Guard for a specific purpose, under specific Federal Rules and Regulations (CFR) for a specific route or body of water.
Certification
The act of attesting that a vessel has met specific legal requirements by the issuance of various certificates or validation of documents by certain governmental or private agencies.
Channel
That portion of a waterway that is naturally or artificially deepened to permit safe navigation within certain limits.
Charter In
To lease a boat or barge from an outside company.
Charter Order
Document utilized to evidence agreement of the specific time charter economic considerations and special provisions for a single voyage booked under a Master Agreement. It is usually in the form of an amendment to a Master Agreement.
Charter Out
To lease a boat or barge to an outside company.
Charter Party
A contractual agreement between two entities for the purpose of renting, hiring, or leasing the exclusive use of a vessel.
Chemical Protective Clothing (CPC)
Respirator with organic (black or yellow) vapor cartridge (half and full-face), Slicker suit, rubber gloves, rubber boots, and goggles if using a half face respirator. A urethane apron may be substituted for a slicker suit for Benzene and Benzene Mixture cargoes.
Chief Engineer
Ship personnel authorized to accept and sign for bunker deliveries. This individual is usually responsible for all machinery in the engine room and on board the vessel.
Chock
A heavy metal casting through which lines may pass for mooring or towing. There are three types of chocks – Open chock, Closed chock, Roller chock
Classification
The certification process as administered by certain international agencies whereby a vessel is designed constructed and maintained to an agency’s requirements.
Clean Barge
Term for a barge used to carry clean petroleum products such as diesel, gasoline and petrochemicals.
Cleat/Kevel
A metal fitting with two projecting horns around which a rope may be tied. It is typically welded along or near the gunwale of a barge.
Clip
A small steel bracket used for securing or reinforcing.
Coaming
A watertight, raised framework around an opening in the deck of a vessel.
Cofferdam
The space in a vessel between two closely located parallel bulkheads.
COFR
Certificate of Financial Responsibility; a document issued by U.S.C.G. to a company for a vessel or a fleet of vessels, giving evidence that the vessel owner/operator has met the financial requirements for oil spill cleanup costs as contained in the Oil Pollution Act of 1990. Usually required for all vessels 300 TONS or more.
Coils
A system of small diameter pipes installed inside a liquid cargo tank for the purpose of heating the cargo by means of hot oil or steam.
Cold Water Wash/Chemical Wash
Pressurized rinse using cold or fresh water; shipyard may use butterworth or there nozzle type.
COREG’s
The international regulations for preventing collisions at sea.
Come home
A convex curvature of the rake sides of a barge that produces a narrower beam at the headlog than the beam of the hull.
Compartment
An interior space of a vessel’s hull which is formed by bulkheads.
Contaminate
When a different type of product is mixed with another and causes the original product to be off spec.
Contract
The instrument that evidences the terms and conditions agreed upon between Kirby Inland Marine, Inc. and the customer under which transportation services are provided to the customer.
Contract Administration Form
Internal document utilized as an information cover sheet in the processing of long term contracts and amendments.
Contract of Affreightment
A contract of affreightment is an agreement for carriage of goods by water or air. A contract of affreightment shall employ a bill of lading, a charter party, or both in order to ship the goods. A contract of affreightment sets forth the obligations and rights of a vessel owner and a merchant. The vessel owner agrees to provide cargo space at a specified time and rate to the merchant who is liable for payment whether or not the cargo is ready.
Cross Channel
To move product between two different docks within the same harbor.
Hose Test Date
The date of the Annual Hose Test. All hoses used to transport product on USCG certified barges must be tested to 1 ½ times their operating pressure every 12 months.
D
Day Rate
The term used when the revenue is determined by the days the equipment is used.
Day marker/Day beacon
A marker used as an aid to navigation that is normally square or triangular in shape. Square day marks are red while triangular day marks are green. Both have reflective borders that show their color at night.
Deadman
An object such as an anchor, piling or concrete blocks buried on shore to which lines are attached for moorings.
Deadrise
The upward slope of a vessel’s bottom occurring when the centerline is deeper than the bilge knuckle; provided to facilitate removal of liquid cargo.
Deadweight Tonnage
The cargo capacity of a vessel.
Deck Barge
A barge that carries dry bulk products on a flat deck.
Deck Button
A round, steel fitting affixed to a vessel’s deck, designed to secure or guide cables for making up barge tows.
Dedicated Tow
Movement of barge(s) between two points by the use of a boat’s exclusively assigned to that movement. A “dedicated” boat offers greater control of barge movements than a “tramp” tow, but generally at a higher cost.
Deionized Water Rinse
Non-pressurized rinse; shipyard uses deionized water.
Demurrage
A charge assessed for detaining a vessel beyond the free time stipulated for loading or unloading.
Detention
The period of time that an owner or charterer is deprived of the use of his vessel as a result of actions of another party.
Dinner-bucket Boat
A boat that does not have a galley or only has limited crew quarters. These boats generally work daylight hours only.
Dirty Barge
A barge used to carry petroleum products such as crude oil, condensate, cat feed, No. 6 oil, bunkers, etc.
Discharge
To unload a product from a barge.
Docking Tug
A tugboat, which assists a large seagoing vessel to and from its berth.
Documentation
The process of licensing a vessel by enrollment or registry, resulting in the issuance of a vessel’s Certificate of Documentation. Vessel documentation is typically required in order to receive a First Preferred Maritime Mortgage from a lender.
Dolphin
A cluster of piles driven into the bottom of a waterway and bound firmly together for the mooring of vessels.
Doubler
A steel plate installed on an existing structural plate used to strengthen the base for deck fittings or to repair a damaged area.
Double-rake Barge
Neither end is square. (See Rake.)
Double-skin Barge
A barge with a void space between the cargo tanks and the sides and bottom of the hull.
Downtime
Time that equipment is not moving due to repairs. (See Allowed Downtime.)
Draft
The depth of a vessel’s keel below the waterline; often expressed as light draft, or conversely, loaded draft.
Draft Marks
The numerical markings on the sides of a vessel at the bow and stern which indicate the amount of water the vessel draws.
Drip Pan
An open container located on deck under the ends of a pipeline header to retain cargo drippage. Required on all U.S.C.G. certified tank barges.
Drydocking
The removal of a vessel from the water to accomplish repairs or inspections.
Dumb Vessel
A vessel without means of self-propulsion.
Dunnage
Any materials used to block or brace cargo to prevent its motion, chafing or damage in order to facilitate its handling.
E
EHL
East of Harvey Lock; used with mileage designations on the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway, Harvey Lock being mile zero.
Emergency Signaling Devices
Hand held radio – walkie talkie
Signal flare
Signal smoke
Whistle/Horn
End Piece
A term used to describe a barge that has one square end and one raked (slanted) end (single rake barge).
Expansion Trunk
A raised enclosure around an opening in the top of liquid cargo tank that allows for heat expansion of the cargo.
F
Face Wire
A cable fastened from the boat to the barge, which makes them secured to each other.
Face Up
Secure the towboat to the barges.
Fairing
Re-forming distorted steel to its original form or shape.
Fairlead
A device consisting of pulleys or rollers arranged to permit reeling in of a cable from any direction; often used in conjunction with winches and similar apparatus. A chock is a fairlead.
Fender
Any device used to absorb and distribute shock in order to prevent chafing between a vessel and another object (may sometimes be called a bumper).
Flame Screen
A corrosion-resistant fine wire mesh screen used to cover certain openings (usually vents) of a tank vessel to prevent the passage of flame into the tank. Flame screens should be checked and cleaned often.
Flange
That portion of a steel shape which projects at a right angle to provide strength or a means of attachment to another part.
Flare
Method used to remove pressure and vapors to a specified percentage level. To burn off vapors remaining in a pressure barge after unloading; also when loading cargoes that require the vapor to be recovered. Most flare towers use natural gas to enrich the burning process. The vapors are piped to a flare tower at a refinery or shipyard.
Fleet Boat
A boat that primarily tends tows within or otherwise services a fleeting area.
Fleeting Area (Fleet)
A designated portion of a waterway where vessels are regularly moored and tended.
Floodgate
Gates on the side of a canal that open and close to control water flow.
Flush Lines
Water is flushed through the pipelines and then stripped out of the tanks.
FOB
Free on Board. Seller or shipper of product or merchandise places product onboard without cost to the buyer or consignee.
Fogbound
Immobilized by heavy fog.
Freeboard
The distance from the waterline to the main deck of a boat or barge.
Freeing Port
A large opening in the bulwark on an exposed deck of a vessel which provides for the rapid draining of water from that deck.
Free Time
Allotted time for loading or unloading given to a customer when figuring demurrage.
Fresh Water Rinse
Non-pressurized cold water rinse.
Fuel Base
The agreed upon price of fuel at a specific date that is used to determine rates on a fully found contract tow. When the price of fuel increases above the fuel base, the rate on the tow will increase per agreed upon terms. Conversely, the rate will decrease with a decrease in the fuel price.
Fuel Transfer Diagram
A schematic of the vessel’s fuel system including fueling ports and vents.
Full Cycle
A cycle which involves turning on a heater on high burn, bringing the temperature up to a preset level, and waiting until heater automatically shuts off high burn and switches to low burn to maintain temperature.
Fully Executed
A term used to indicate a contract has been signed by all parties.
Fully Found
When the rate paid for the use of a boat or tow includes fuel.
FWPCA
Federal Water Pollution Control Act, the U.S. federal statute that establishes the legal and financial responsibilities of those persons or companies which discharge or dispose of oil or hazardous substances into or upon the navigable waters of the U.S. Primarily administered by the U.S. Coast Guard.
G
Gas Free
The process of removing all hazardous gases and residues from the compartments of a vessel in order to receive the hot work permit (this will be noted on the Gas Free Certificate). This is usually done at a shipyard.
Gas Free Certificate
Certificate that states the vessel has been checked by a certified marine chemist. Also states information about the condition of a vessel as far as entry and hot work.
Gauge
A waterway marker that measures the level of the water in foot increments; also refers to the specific measure on the gauge.
Gauge Tape
A tape line which is used to measure liquid in a cargo tank.
GIWE
Gulf Intracoastal Waterway East: between New Orleans and Panama City.
GIWW
Gulf Intracoastal Waterway West: between New Orleans and Brownsville.
Government Personnel
Includes but is not limited to the U.S. Coast Guard (COTP, Inspectors, VTS, etc.), U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (Lockmaster, etc.), Port Authority (Harbormaster, etc.), and State Highway Department (Bridge tender, etc.).
Gravitating
1. Loading a product into a barge by gravity rather than using shore side pump. 2. Moving product from compartment to compartment.
Gross Tons
The volume measurement of the internal voids of a vessel wherein 100 cubic feet equals one ton.
Gunwale (Gunnel)
That part of a barge or boat where the main deck and the side meet.
Gusset
A steel plate used for reinforcing or bracing the junction of other steel members.
H
HH2S
Hydrogen Sulfide: A highly toxic, flammable, colorless gas recognized by its characteristic foul, rotten egg odor.
H2S PEL
The permissible exposure limit for hydrogen sulfide gas is 10 parts per million (PPM) time weighted over an eight-hour workday.
H2S STEL
The short-term exposure limit (STEL) for hydrogen sulfide gas is 15 parts per million (PPM) for any 15 minute time period.
Harbor Boat
Any powered vessel that is used primarily in harbor operations.
Hatch
Removable watertight covers over the cargo hold and voids of a vessel.
HAZMAT
Hazardous Material
Hawser
A large circumference rope used for towing or mooring a vessel or for securing it at a dock.
Head of Navigation
The uppermost limit of navigation from the mouth of a waterway.
Headlog
The reinforced vertical plate that connects the bow rake bottom to the rake deck of a barge. The actual end of the barge
High Viscosity Cargo
Cargo with a resistance to flow freely, having a minimum loading temperature of 200ºF and requiring barge preheating.
Hip Towing (Hipping)
A method of towing whereby the vessel being towed is secured alongside the towboat.
Homeport
The port city which is the home base of a vessel or the city from which it is documented.
Hopper Barge
An open compartment barge used for carrying bulk cargo.
Horsepower
A standard unit of power which is often classified in connection with engines as brake, continuous input, intermittent, output, or shaft horsepower.
Hose
A flexible tubing made of rubber, metal or suitable material which is used to move liquid or gas products between the dock pipeline and the barge pipeline or between two (2) barges (crossover hose).
Hot Oil Barge
A barge equipped with a system that consists of a boiler, which burns fuel oil and fires a burner which transmits heat to the special oil circulated through heating coils. This system is used to maintain the minimum temperature of certain heavy petroleum products.
Hot Water Chemical Wash
Pressurized wash; shipyard uses detergent.
Hot Water Wash
Pressurized rinse using hot water; shipyard may use butterworth or other nozzle type.
Hull
The main body of a vessel that provides floatation.
I
ICC
Interstate Commerce Commission; a U.S. governmental agency which regulates the domestic transportation of certain commodities.
ICWW
Intracoastal Waterway. A canal that runs along a specific coast inland.
IDLH
Immediate Danger to Life and Health.
Incident
Any occurrence causing actual or possible downtime, damage, or catastrophe.
Inert
Introducing Nitrogen to reduce Oxygen levels to a specified percentage; sales to specify Oxygen % or Dew Point; sales to specify who will verify the cargo tank’s atmospheric condition; same as Purge.
Inland Waters
Considered to be the canals, lakes, rivers and their tributaries, and bays and sounds of the land mass of a country.
Integrated Tow
A tow of box-ended barges which, as a complete unit, is raked at the bow, boxed at the intermediate connections, and boxed or raked at the stern.
J
K
Keel
The lowest structural member of a ship or boat which runs the length of the vessel at the centerline and to which the frames are attached.
Keel Line
An imaginary line describing the lowest portion of a vessel’s hull.
Kevel
A heavy metal deck fitting having two horn-shaped arms projecting outward around which lines may be made fast for towing or mooring of a vessel.
Knot
One nautical mile per hour; used as a unit of measurement in expressing the rate of speed of seagoing vessels and the relative speed of water currents.
L
Landing
An improved waterfront property which facilitates loading, unloading and servicing of vessels.
Lay time
The time when a tow is standing by awaiting dock space.
Lead Barge
The head or first barge of a tow.
Light Boat
A towboat without a barge in tow.
Lighter
A vessel, usually a barge that is used in loading or unloading a ship or another barge.
Light Screen
A structure surrounding a vessel’s navigation light so as to shield the light from view at certain points of the compass as required by navigational regulations.
Light Stand
A structure on a vessel used to hold navigation light.
Limber Hole
A drain hole near the bottom of a frame or bulkhead.
Lines
The ropes or cables used on a vessel for towing, mooring or lashing.
Line Haul
Movement of normal products with a boat and barge(s). The tow usually works for one customer for a specific period of time.
LNG
Liquefied natural gas.
Load
To put product into a barge.
Load line
The safe level to load a barge as determined by the American Bureau of Shipping.
Load line Marks
A set of permanent markings on the side of an oceangoing or Great Lakes vessel which denotes its maximum legal operating draft under certain specified conditions that is determined by one of the internationally recognized assigning agencies such as ABS.
Lock
An enclosure on a river or canal, with moveable, watertight gates through which vessels pass and proceed from one water level to another by raising or lowering the water within the lock chamber.
Lock Clause
A section of a contract that states the demurrage will begin after a tow is at a lock after a certain length of time.
Lock Gate
A movable, structural barrier to hold back the water in a lock chamber.
Lockmaster
Person employed by Corps of Engineers who is in charge of ensuring safe passage of vessels through locks.
Logbook (Logs)
The official records of the daily operations of a manned vessel kept in detail by the master.
Lunch Bucket Boat
See Dinner Bucket Boat
LPG
Liquefied Petroleum Gas. A compressed gas that consists of flammable hydrocarbons (such as butane and propane) and is used as fuel or as raw material for chemical manufacturing.
M
Make-up
The act of positioning and securing of the vessels that form a tow.
Maltese Cross A-1
The designation used by ABS which signifies that a vessel has met the classification requirements of that agency.
Manhole
A framed opening in the deck of a vessel which primarily provides access for a man.
Manhole Cover
A cover which seals a manhole and is usually designed to lock in place by twisting or using a center bolt, stud bolts or dogs.
MARAD
The U.S. Maritime Administration.
Marine Chemist
One who is certified to perform inspections in accordance with the standard for the control of gas hazards on vessels to be repaired as adopted by the National Fire Protection Association?
Marine Chemist’s Certificate
The documentation of a vessel’s inspection by a marine chemist and his assignment of standard safety designations to the inspected compartments or spaces.
Master
The Captain of a vessel, the person who has complete charge of and authority aboard an operating vessel.
Master Contract
Contract, usually for an indefinite period of time, in which a company and the customer agree to the general terms and conditions under which transportation services will be provided to the customer. The commercial details and special provisions relative to an individual voyage or trip are confirmed using Charter Orders or Affreightment Orders, as appropriate.
Manhole assembly raised trunk-dogged type
Manhole assembly center bolt type
T-Handle style Center bolt style
Manhole assembly twist-lock type
Maximum Allowable Working Pressure
A design standard which represents the highest pressure a piece of equipment should be exposed to (MAWP).
Mile marker (Mile board)
A marker set up to indicate distances in miles along a waterway.
Minimum Required Cargo Discharge Temperature
The lowest cargo temperature permitted to allow the barge pump to discharge the cargo as determined by the salesman.
Model Hull
A type of hull design in which the form is molded, curved and shaped into a pointed stem and rounded stern.
Mooring
The act of making fast a vessel with lines or anchors; or a place where a boat can be moored.
Mopping
To clean out the remaining product in a barge after discharging. Usually this consists of only puddles.
MRGO
Mississippi River Gulf Outlet, the deep draft waterway connecting the New Orleans Inner Harbor Navigation Canal to the Gulf of Mexico.
N
Nautical Mile
A unit of length used in sea navigation equal to 1,852 meters or approximately 6,076 feet.
Navigable Waters
Those waterways upon which commercial or private vessels are able to operate in their customary mode of navigation.
Navigation Lights
Those lights aboard a vessel or a tow required to be shown at night and at other times of restricted visibility.
Net Tons
The gross tons of a vessel less deductions for certain specified non-cargo spaces resulting in a net-volume capacity of 100 cubic feet per ton.
Nitrogen Bottles
Used when Nitrogen bottles need to be filled, removed, or added; Sales to specify which one (in comments).
O
OCMI
Officer in Charge of Marine Inspections at a U.S. Coast Guard Marine Inspection office. Such offices are located in a number of U.S. ports.
Odor Free
Barge is free from odor.
Off Spec
When specifications of the product are not acceptable with the specifications of the customer.
Official Number ****
The registration number assigned by the U.S. Coast Guard to a U.S. documented vessel and which is permanently marked on the main beam of that vessel. The official number is issued only once and can never be changed.
Offshore Waters
A common term for those waters which are beyond inland water limits and have the technical classification of “Oceans.”
One Year From Completion
Any twelve month period beginning on a specific date and ending on the same date of the following year.
Optimum Fuel Burn
Best balance between vessel speed and fuel consumption.
Optimum Speed
Highest speed consistent with Traffic, Safety, and Navigational Hazards.
Outside Tankering Service
Third party company independent of Kirby Inland Marine or the customer, hired to transfer product to or from a barge.
P
Packing
A product that is wrapped around a shaft to keep the unit from leaking; generally used in some pumps and valves. Resembles a rope coated with an oily wax substance.
Pad-eye
A steel fitting formed by a flat doubler plate and vertical steel member containing a circular opening. Pad-eyes come in many shapes, sizes and designs. Below is an example.


PEL
Permissible Exposure Limit. (1.0 PPM Benzene - 8-hour time weighted average).
Pelican Hook
A hinged hook held closed by a ring and used to provide the quick release of an object which it holds. Usually on both ends of the ratchet used to make tow.

Pertinent Spill Information
Includes, but is not limited to, the following:
- Name of the person reporting the spill
- Name of the towing vessel
- Name of the barge(s) involved
- Time of the spill
- Location and source of the spill
- Identity of the product spilled
- Course, speed and intended track of the towing vessel
- Estimate of quantity of product spilled on the deck and/or in the water
- Existing or potential hazard (fire, explosion, etc.) if any
- Corrective action being taken
- Weather conditions on scene
- Current condition of the vessel
Piling Cluster (Cluster Pile)
A group (usually five or more) of piles that are driven into the ground to which mooring lines are tied when docking a barge or a ship. The piles can be steel, wood, or concrete.
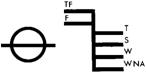
Plimsoll Mark
This mark was invented by Samuel Plimsoll in 1870. A load line or a set of load-line markings on an oceangoing vessel indicating the greatest depth to which a vessel may be loaded under certain circumstances and in different seasons and different types of water.
TF = Tropical Fresh
S = Summer Load Line
F = Fresh
W = Winter Load Line
T = Tropical Load Line
WNA = Winter Load Line North Atlantic
Port
The left-hand side of a vessel when facing forward; a city having a harbor for vessels; a port hole.
Posted Pilot
When a pilot is familiar with the geographic configuration of the waterway; the type and size of vessel using the waterway; the abundance of absence of aids to navigation; background lighting effects, known hazards involved including waterway obstructions or constrictions such as bridges, narrow channels, locks, or sharp turns and any factors, including under and above water clearance unique to the waterway; knows the speeds prudent for the weather, visibility, and traffic density, tow draft, speed of current, possibility of wake damage and local speed limits.
Power Cost
The operating cost of the boat that moves the barge(s).
PPE
Personal Protective Equipment
Propeller walk
The term for a propeller's tendency to rotate a boat as well as accelerating it forwards or backwards. A right-handed propeller (clockwise rotation from stern view) will push the stern of a boat to the starboard.
Pre-staging
The use of boats to expedite barges from fleeting areas with advance job knowledge.
Prime
To prepare pump for operation, as by filling the pump well with cargo.
Propeller
A mechanical device having radiating blades which is mounted on a revolving, power-driven shaft for the purpose of propelling a boat; also called a screw or wheel.
Pumping Rate
Generally, the rate in barrels per hour that a barge will discharge product.
Purge
Introducing Nitrogen to reduce Oxygen levels to a specified percentage; sales to specify Oxygen % or Dew Point; sales to specify who will verify the cargo tank’s atmospheric condition; same as Inert.
Pushboat
A highly maneuverable, inland water, shallow draft towboat usually designed with a square bow and towing knees which facilitate its primary method of towing which is pushing.
Push Knee (Tow Knee)
A vertical, reinforced steel structure installed on a vessel to facilitate push towing. The height of the knee allows for variance in freeboard between vessels.
PV Valve
Pressure vacuum relief valve; a valve which automatically regulates the pressure or vacuum in a tank.
Q
R
Raised Rake
The rake of a barge which has sheer.
Raised Trunk
Center cargo compartments that are raised above the rest of the deck.
Rake
The configuration of the end of a barge or boat in which the bottom slopes upward to meet the headlog or sternlog.
Reach rod
A steel rod which connects an above deck valve handle to a below deck valve.
Registered
Pertaining to certain vessel data calculated under specific rules and officially documented, such as registered length.
Regulated Area
Any area where the potential exposure to benzene is 1.0 PPM for 8 hours or 5.0 PPM for 15 minutes.
Reversible Time
In an affreightment contract, the allowed free time given as a total number of hours which will apply for both loading and discharging when figuring demurrage.
ROB
Remaining On Board. Refers to cargo which is left inside a barge after discharging.
Rub rail
A protective railing on the hull of a vessel which is used for fendering.
Rules of the Road
A code governing vessels as to the lights to be carried, the signals to be made and their safe and proper navigation in order to avoid collisions. These regulations are known as unified rules, which govern the colreg, the high seas and connecting waterways.
Running Lights
Those lights required to be shown at night aboard a vessel or a tow while underway.
S
Sailing Line
The preferred course for safe and efficient navigation in the channel of a waterway.
Scupper
A drainage opening cut flush with the deck of a vessel through the bulwark or bin wall.
Seaworthy
The reasonably staunch, sound, and fit condition describing a vessel’s capability to safely carry its cargo and complete its intended voyage or use.
Semi-integrated Barge
A barge that is raked at one end and boxed at the other end.
Shackle
A u-shaped metal fitting used as a connection for line, cable or chain that has a pin secured through its end by a nut, cotter pin or screw threads.
Sheer
The upward curvature or angle of a vessel’s deck at the bow or stern.
Shifting
The short movement or transfer of a vessel within a harbor or mooring area.
Shore Tankermen
Independently employed individuals who load and discharge barges.
Shoreside
People, operations or equipment on land as opposed to on boats or barges.
Single-skin Barge
A barge that has only one metal shell. It will have a void stern compartment and a bow rake compartment.
Slope sheet
The sloped vertical steel plate forming the end of the barge void compartment that is part of the rake bulkhead.
Slop Tank
A tank located normally on the deck of a tank barge which holds product that is stripped from the barge after discharge (See Bottoms).
Spill
When product from a barge spills onto the deck or into the water around the barge due to a hole in the barge, leak in the transfer system, or if too much product is loaded into the barge and is not contained in the barge cargo compartments.
Spot Contract
A term used to indicate a contract covering one voyage.
Spot Market
A very general term that refers to work done for customers that is not long-term work.
Spot Requirement
An inquiry to move cargo on one-time basis.
Spray Load
A method of loading LFG cargoes through the cargo tank vapor piping to minimize cargo tank pressure.
Spring Line
A line secured amid ship leading forward or aft between barges to prevent barges from surging forward and aft.
Spud
A steel or wooden post or pile that is placed vertically through a well in the hull of a vessel and which, when lowered to the bottom of the waterway, anchors the vessel.
Stand-by
Adj. – Waiting in readiness or reserve. Noun – An order or signal for a vessel to stand by.
Starboard
The right-hand side of a vessel when facing forward.
Steam
Shipyard to steam cargo to specified temperature; sales to specify temperature.
Steamboat Ratchet
A sleeve, internally threaded at the ends and with attached eye-rods equipped with a ratchet used to turn the sleeve, thereby pulling the rods towards each other.

Steam Coils/Steaming Coils
Pipes located on the bottom of the cargo tanks of a barge through which steam can be pumped in order to heat the product in the barge to facilitate discharge.
STEL
Short Term Exposure Limit. 5.0 PPM, 15 minute exposure time. Maximum four (4) times per eight (8) hour shift with minimum between exposures of one (1) hour.
Stem
1. Transportation requirement outlining product specifications, product volumes, ships destination and ETA. 2. The main vertical structural member which forms the foremost part of a boat’s model bow.
Stern
The aft or rear end of a vessel.
Sternlog
The reinforced, vertical shell plating which connects the stern rake bottom to the rake deck of a barge.
Straight Shot
Straight load, no blend.
Strake
A longitudinal or transverse row of steel hull plates.
Strapping
The calibrated measurement of the compartment of a tank barge to determine the exact number of barrels or gallons it will hold.
Strapping Table
A chart used to convert readings of liquid levels in the tanks of a barge to volume measurements of that liquid.
Strip
Boat or shipyard to open valves, drop pipeline, then strip as much liquid as possible from cargo tanks with onboard stripping system; there will be wet spots and small puddles.
Strip and Blow Dry
All liquid removed from cargo tanks, tanks and lines blown dry.
Strip and Squeegee
Barge is stripped then squeegeed; tanks are not dry; sales to specify in comments if “squeegee only” is required. Only applicable to lubes.
Strip Overhead
Shipyard or qualified boat to strip as well as possible and then use stripping wand and/or mops to get remaining visible liquid. There may be product left where it can’t be seen or reached. Barge is not dry. May incur vapor control charges if at a shipyard.
Stripping
Removal of bottoms from a barge after completion of discharge of product to a dock.
Stripping System
A piping system on a barge that will remove bottoms after discharging, and store the bottoms in a slop tank.
Superstructure
The structural part of a boat above the main deck.
Supplied Air Respirator
Equipment that delivers breathing air at positive pressure to a full-face respirator.
Survey
A critical examination or inspection of a vessel, cargo, or marine structure for the purpose of ascertaining desired facts and conclusions when necessary.
Survey – Condition
A survey that determines in some detail the specific condition of a vessel or of cargo; usually performed at the commencement or termination of charters or voyages for the agreed mutual benefit of various parties.
Survey – Damage
Determines the exact extent of damages incurred and specifies repair requirements.
Surveyor
A qualified marine inspector who performs surveys.
Sweep Boom
Elongated absorbent material (pad) with rope handle, approximately ninety (90) feet long, that resists water and soaks up hydrocarbon cargoes.
T
Tag out
The placement of a tag device on an energy isolating device, in accordance with the established procedure, to indicate that the energy isolating device and the equipment being controlled may not be operated or used until the tag device is removed.
Tank
An enclosed space used for holding liquids.
Tankering
The act of loading or transferring product into a barge or discharging or transferring product from a barge.
Tankering Codes
A list of reason codes defining why a shore Tankerman is needed. A copy of the tankering codes can be found in the Dispatch Information Manual.
Tankerman
A person licensed by the U.S. Coast Guard to transfer product to or from a barge.
Tender
Notifying a dock that a tow is ready to go to the dock for loading or discharging.
Tender Codes
Information delivered by Sales determining when a barge/tow can or cannot be tendered. A copy of the tender codes can be found in the Dispatch Information Manual.
Term
Generally, a word used to indicate a fixed period of time for which a contract will be in force.
Time Charter
A contract by which a vessel is chartered to another party for a specified time or use. Charter Hire is invoiced based on a specified rate for the day or a portion thereof. Time charters do not contain free time and demurrage provisions.
TLV
Threshold Limit Value
Tow
To push or pull vessels on a waterway; also refers to the unit comprised of the towing vessel and the vessels being towed or only the vessels being towed.
Tow Information
Information regarding the status of tow (e.g., loads, empties, cargoes, etc.)
Towboat
Any powered vessel that is used for towing.
Traffic
The position or location of the tows during a day as recorded by dispatchers from various radio calls. The chronological record of vessel activities.
Tramp Tow
Movement of barge(s) between two points by including it/them in a tow of a boat and other barges going in the same direction (contrast with “dedicated” tow). It is sometimes necessary to transfer barges being “tramped” from one boat to another to achieve the desired route and destination. Cost is generally less than the use of a “dedicated” boat, but control of the timing of barge movements is also less.
Tramping
Towing for Others. Moving barges from one location to another at a fixed rate.
Transom
The framed plate forming the stern of a square ended boat or barge.
Transverse Truss
Internal barge support frames laying crossways the length of the barge. Usually consisting of upper and lower channel chords/beams connected to each other with a combination of vertical and diagonal members of different sizes and strength depending on design loads.
Trip Confirmation
Internal document utilized to communicate specific information on a trip negotiated between a Sales Manager and a customer.
Tripping
The operation of tying off one or more barges in a tow in order to move the remaining barges in the tow through a lock or bridge when conditions are not safe to move the complete tow.
Truss
A rigid framework of horizontal, vertical and diagonal structural members designed to support loads and reinforce a vessel’s hull. Usually consist of upper and lower channel chords/beams connected to each other with a combination of vertical and diagonal members of different sizes and strength depending on design loads.
Tugboat
A model hull towboat of relatively deep draft used primarily for pull towing and designed for navigation in open or unprotected waters.
Turnbuckle
A connecting device generally used with cable or chain and which takes up slack by rotating on its screw threads.
U
Ullage Opening
A small, covered opening in the top of a cargo tank through which measurements are made to determine the level of the liquid in the tank.

Underway
In motion from a standstill.
Unit Tow
Usually a three-barge, integrated tow consisting of bow, center and stern sections.
U.S.C.G.
United States Coast Guard
V
Vapor Controlled Transfer
Vapors returning from a barge to a dock, shore tank, or vented through the vent stack.
Vapor Tightness Certificate
Document indicating a barge has been pressure tested for vapor tightness in the last twelve (12) months.
VCG
Vertical center of gravity; an important computation used in the determination of the stability of a vessel with its cargo.
Vent
1. To open hatches to the compartments on a barge in order to air out and dry out the tanks. Also, an opening in a tank or compartment (usually a pipe) preventing over or under pressure of the tank or compartment. 2. Ventilate or blow for entry. Barge does not have to be dry.
Vessel Log Book
An informal diary chronologically listing all events of the day in a rough note format.
Viscosity
The degree to which a fluid resists flow under an applied force. There are five measurements of viscosity: Redwood (Seconds), Saybolt Universal (SSU), Saybolt Fural (SSF), Engler and Kinematic (CST).
VRP
Vessel Response Plan; a U.S.C.G. approved set of guidelines for responding to a spill or potential spill of oil from tank vessels, including training and testing procedures, as mandated in the Oil Pollution Act of 1990.
VTC
Vessel Traffic Control; a central control system used in some ports to safely direct navigation.
W
Watertight
Of such construction or fit as to prevent the passage of water, except when structural discontinuity, physical rupture or purposeful opening may occur.
Wheel
Another term for a propeller; also a boat’s steering wheel.
Wheelhouse
The upper section of a boat where the Captain steers the boat.
WHL
West of Harvey Lock; used with mileage designations on the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway, Harvey Lock being mile zero.
Wind bound
When a tow stops due to high wind and the boat does not have enough power to keep the tow moving.
WOT
Waiting on Traffic
WOW
Waiting on Weather





 Smith Maritime's vessels operate primarily between the U.S., the Caribbean & South America. More recently to several ports in Europe, the Mediterranean Sea & Pacific Northwest. Our history is one of dedicated service with a superior loss record. Our services include ocean and coastal towing, pipe & cable laying, submersible operations, cargo & dredge ops, demolition, harbor, anchor and buoy handling, and most exciting of all, salvage and rescue.
Smith Maritime's vessels operate primarily between the U.S., the Caribbean & South America. More recently to several ports in Europe, the Mediterranean Sea & Pacific Northwest. Our history is one of dedicated service with a superior loss record. Our services include ocean and coastal towing, pipe & cable laying, submersible operations, cargo & dredge ops, demolition, harbor, anchor and buoy handling, and most exciting of all, salvage and rescue.